Here’s how to send an encrypted email:
Encrypt Gmail:
- Open Gmail and click Compose.
- In the email window, click the lock icon with a clock at the bottom (Confidential mode.)
- Set an expiration date and choose whether a SMS passcode is required.
- Click Save
- Write your email and hit Send.
Encrypt Outlook:
- Open Outlook on the web and click New message.
- Click the Encrypt button (a lock icon) above the message area.
- Choose Encrypt or Encrypt & Prevent Forwarding.
Write your email and hit Send.
Email is essential for how we communicate today, but it’s not without risks. While we rely on email for everything from casual chats to important work matters, it’s good to remember that these messages aren’t always as private as we think.
Email encryption offers a powerful way to protect your information, essentially scrambling your emails so only the intended recipient can read them. This article will walk you through the ins and outs of email encryption, giving you the tools you need to encrypt an email and keep your email communications secure.
What Is Encrypted Email?
Let’s learn how to encrypt email in Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo and on iOS devices:
How to Encrypt Email in Gmail
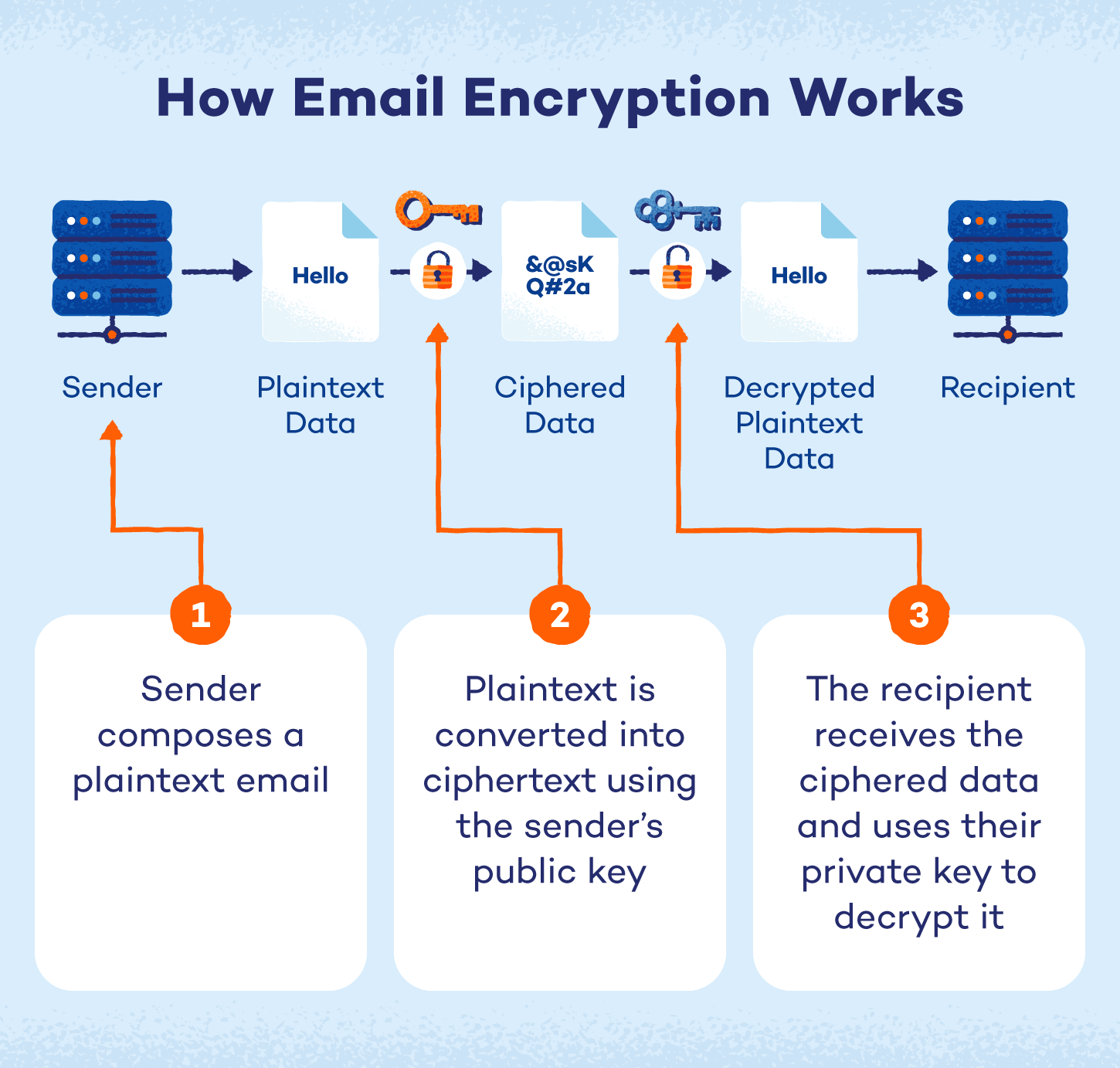
Email encryption is essentially a way to transform your email messages into an unreadable format so that only the person you’re sending them to can read them. Here’s how it works:
- Compose your regular email: This is the message you want to send, known as the plaintext.
- Convert into ciphertext: Encryption uses a special algorithm and key to scramble your plaintext into ciphertext, which looks like a jumbled mess of characters.
- Allow only the recipient to unlock the code: The recipient has the key to decrypt the ciphertext back into readable plaintext.
- Ensure your emails are protected: This process protects your emails from being read by anyone who might intercept them along the way.
Encryption relies on public key infrastructure (PKI) to encrypt and decrypt messages. Each user is assigned two keys:
- Public key: It’s stored on a public key server and is accessible to anyone. When someone sends you a secure email, they use your public key to encrypt it.
- Private key: It’s safeguarded on your computer or device and is accessible only to you. This key is essential for decrypting emails you receive.
You can also use your private key to create a digital signature, verifying to recipients that the email genuinely came from you.
How to Encrypt an Email in Gmail

Because Gmail’s S/MIME functionality is tied to Google Workspace accounts and administrator controls, we can’t provide general how-to steps for personal Gmail users. However, we can explain the process to encrypt gmail for those using a Google Workspace account.
The process will depend on whether your organization uses hosted S/MIME (enhanced encryption) or client-side encryption (CSE/additional encryption). Your administrator will likely provide specific instructions.
For Google Workspace users (S/MIME enabled by your admin):
- Check for enabled feature: If your administrator has enabled hosted S/MIME, the option to encrypt might appear automatically when composing emails. Look for a lock icon or an “Encrypt” button within the compose window.
- Encrypt: If the option is available, simply click it to encrypt your message. Gmail will handle the encryption using keys managed by Google.
Client-side encryption (CSE/additional encryption):
- Administrator setup: CSE requires significant setup by your organization’s IT administrator. This usually involves installing and configuring key management systems.
- Client configuration (if required): You might need to install specific software or configure your browser to use CSE. Your administrator will provide these instructions.
- Encrypt: Once configured, the option to encrypt should appear in your compose window. The encryption will occur on your device before you send the email.
For personal Gmail users:
As mentioned above, personal Gmail accounts do not have direct access to S/MIME. Confidential mode is the closest built-in feature, but it’s not true end-to-end encryption. For true end-to-end encryption with personal Gmail, use a third-party tool like Mailvelope.
How to Encrypt Emails in Outlook

Encrypting emails in Outlook requires a digital certificate (sometimes called a digital ID). Here’s a simplified overview, but always refer to Microsoft’s official support for your specific Outlook version:
- Get a certificate: You’ll need a digital certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA). This might be provided by your company’s IT department or a third-party provider.
- Install the certificate: Once you have the certificate file, you need to install it on your computer. Outlook usually has an import function for certificates. Microsoft’s instructions will guide you through this.
- Configure Outlook: Open Outlook and go to File > Options > Trust Center > Trust Center Settings > Email Security. Here, you’ll associate your certificate with your email account.
- Encrypt a message: When composing a new email, look for “Options” or “Message Options.” There should be a button or checkbox labeled “Encrypt this message (S/MIME)” or something similar. Click it.
- Send: Compose your email as usual and click “Send.” Outlook will use your certificate and the recipient’s public key (if they have one) to encrypt the message. If the recipient does not have a public key, Outlook will give you the option to send the email unencrypted since the recipient won’t be able to decrypt your message.
Important notes:
- Recipient’s certificate: You can only send encrypted emails to people who also have a digital certificate. Outlook needs their public key to decrypt the message.
- Troubleshooting: Certificate installation and configuration can be tricky, so consult Microsoft support if you have trouble.
- Default encryption (optional): In the email security settings, you can set Outlook to encrypt all outgoing messages (to those who have public keys) by default.
How to Encrypt Emails on iOS (iPhone/iPad)

Encrypting emails on iOS (iPhones and iPads) typically involves using S/MIME, which also requires a digital certificate. Here’s a general guide, but the exact steps might vary slightly depending on your iOS version and email provider:
- Get a certificate: You’ll need a digital certificate from a trusted certificate authority. If your organization provides it, they’ll also provide installation instructions.
- Install the certificate: If you received a certificate file (often with a .p12 or .pfx extension), you’ll need to install it. This often involves emailing the certificate file to yourself, opening it on your iOS device and following the prompts to install it in the keychain.
- Configure mail (if necessary): Some email accounts might require you to enable S/MIME in the Mail settings. Go to Settings > Mail > Accounts > [Your Account] > Advanced. Look for S/MIME settings. If you don’t see these settings, your email provider might not support S/MIME in this way and might require a different setup.
- Encrypt an email: When composing an email, look for a lock icon or an “Encrypt” option. It might be in the “Cc/Bcc” field or under “Options” (sometimes represented by three dots). Tap it to turn on encryption for that specific email.
- Send: Compose your email as usual and tap “Send.” iOS will use your certificate and the recipient’s public key (if they have one) to encrypt the message.
Important notes:
- Recipient’s certificate: You can only send encrypted emails to people who also have a digital certificate. If the lock is blue, the email can be encrypted. If the lock is red, the recipient needs to turn on their S/MIME settings.
- Email provider support: Not all email providers support S/MIME in a way that directly integrates with the iOS Mail app. If you don’t see the S/MIME settings, check with your email provider.
- Mobile device management (MDM): If your device is managed by your company (using MDM), the S/MIME settings might be controlled by your IT department.
- Alternative encryption: If your email provider doesn’t support S/MIME, you might need to use a third-party email app that supports other encryption methods, like PGP.
How to Encrypt an Email in Yahoo Mail
Yahoo Mail doesn’t offer built-in, end-to-end email encryption in the same way as S/MIME or PGP. It does offer some security features (like HTTPS for secure connections) but not message-level encryption.
If you want to send truly encrypted emails using Yahoo, you need to use a third-party tool or service. Here’s how to send an encrypted email in Yahoo:
- Install a browser extension (like Mailvelope): A browser extension can add PGP encryption to your Yahoo Mail in your web browser. This is a good option if you want to encrypt individual emails. Simply install the extension, configure it and then use it to encrypt your messages before sending them through Yahoo Mail. The recipient also needs to have a compatible PGP setup to decrypt the message.
- Use a third-party email client with encryption: You could use a desktop email client like Thunderbird that supports encryption (PGP or S/MIME). Configure the email client to access your Yahoo Mail account, then use the client’s encryption features to encrypt your emails.
- Employ a secure email service: You could use a separate secure email service like Proton Mail for your most sensitive communications. These services have built-in end-to-end encryption. You would not be encrypting the email within Yahoo but sending the encrypted email through a different, secure channel.
Types of Email Encryption
The two main types of email encryption protocols are Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension (S/MIME) and Pretty Good Privacy/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension (PGP/MIME).
Both models work by way of user key exchange — the sender and receiver each have a public and private key for encrypting and decrypting messages. We’ll look at each type more in depth below.
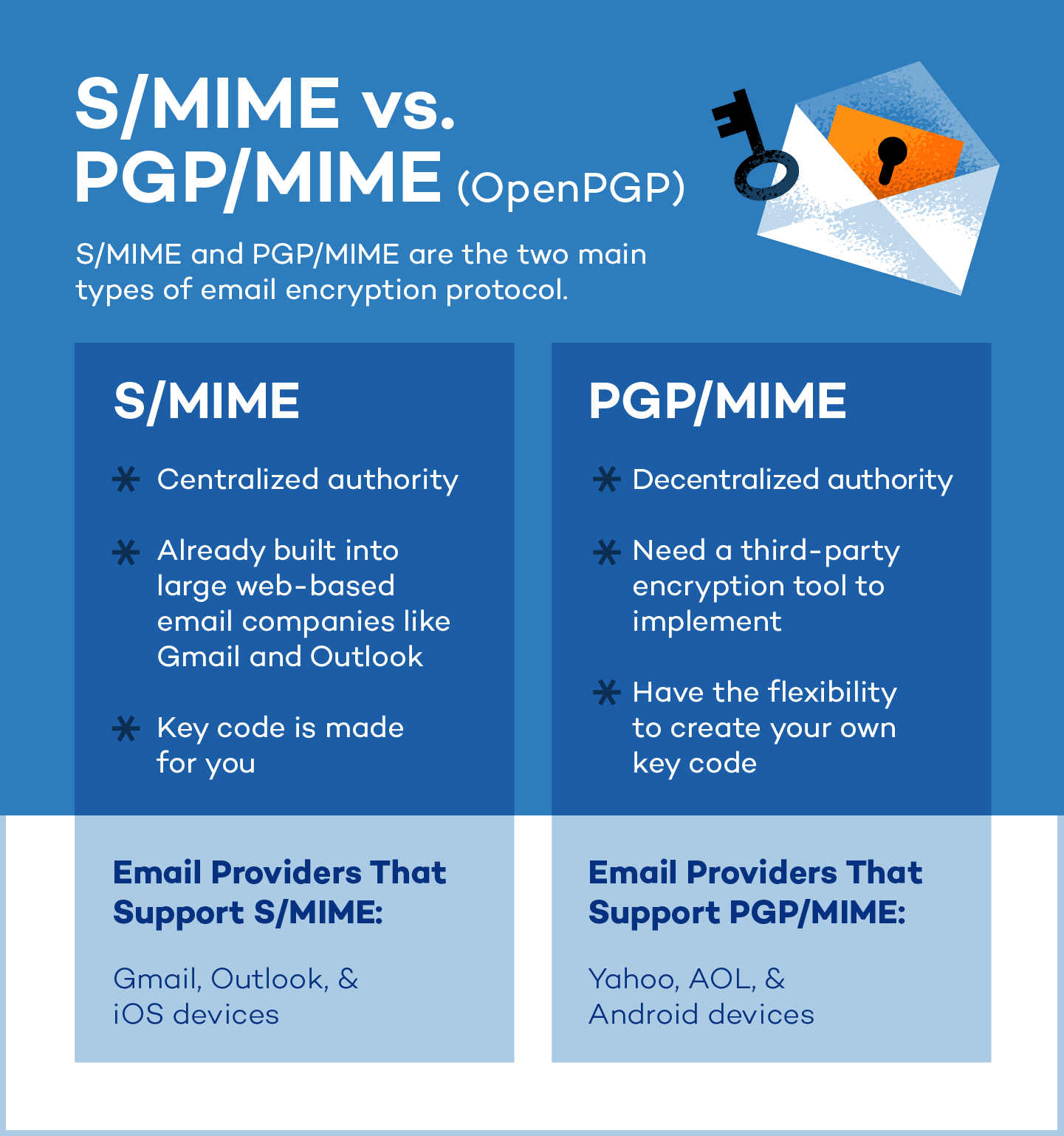 S/MIME
S/MIME
S/MIME is an email encryption tool that’s built right into most iOS devices and used by big email providers like Gmail and Outlook. It relies on trusted organizations to provide the security keys needed to encrypt and verify emails.
Because it’s so widely available and easy to use with common email services, S/MIME is a popular choice for businesses and organizations that need to keep their email communications secure.
PGP/MIME
PGP/MIME relies on a decentralized trust model where everyone manages their own security, giving you a lot of control over how secure your emails are.
However, you’ll need third-party encryption tools to access more flexibility and control. PGP/MIME is most common for personal or organizational use and is compatible with Android devices. Unlike S/MIME, it can also be used in VPNs.
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
TLS is a behind-the-scenes security system that protects your information while it’s traveling across the internet. It’s used for all sorts of online activities, from sending emails to logging into websites.
TLS works differently than S/MIME and PGP/MIME, which code the message itself so no one can read it even if they intercept it. Instead, TLS focuses on securing the connection between you and the email server, preventing eavesdropping while the message is being sent.
Encrypt Email With Third-Party Tools
Email encryption can be done manually or by a secure third–party email service. These third-party tools handle the encryption process for you, often providing a more user-friendly experience than manual configuration. They can also offer additional privacy features, like secure storage and zero-knowledge encryption, giving you greater control over your data.
Here are some email service apps with unique offerings, such as encrypting emails, attachments and contact lists:
- Proton Mail: End-to-end encryption with free and paid plans, offering a strong focus on privacy and security
- PreVeil: Offers military-grade compliance with end-to-end encrypted cloud storage and email across all devices
- Barracuda: HIPAA compliant, catering to health care organizations that need to protect sensitive patient data
- Mailvelope: A browser plug-in allowing you to add PGP encryption to existing webmail services like Gmail
- Virtru: End-to-end encryption for Gmail and Outlook, seamlessly integrats encryption into familiar email platforms
- StartMail: Offers PGP encryption with paid plans, giving users control over their encryption keys
Benefits of Encrypting Your Email
Email encryption is essential for safeguarding sensitive information from cyberthreats, particularly data breaches. In the first quarter of 2023 alone, over 6 million data records were exposed. By encrypting your emails, you’re taking a proactive step to prevent your information from becoming part of these cybersecurity statistics and mitigate potential financial and reputational damage.
Here are some of the benefits of encrypting your information online:
- Protect personal information: Keep sensitive details like addresses, Social Security numbers and financial information out of the wrong hands.
- Safeguard business data: Protect confidential company information, trade secrets and customer data from leaks and breaches.
- Maintain privacy in personal communications: Ensure your private conversations and personal matters stay private.
- Comply with data protection regulations: Meet legal requirements for protecting sensitive data, such as HIPAA, GDPR and other industry-specific regulations.
- Build trust and credibility with recipients: Show your contacts that you take their privacy seriously, fostering trust and strengthening professional relationships.
Other Ways to Protect Your Data Online
With or without an email encryption service, it’s always a good idea to implement security best practices when using email. Keep these tips in mind:
- Use strong and unique passwords: Using complex passwords with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols makes it harder for hackers to guess your passwords and access your personal accounts. Try our password generator to make this quick and easy.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Two-factor authentication (2FA) serves as an additional layer of security for your email accounts. For example, you might enter a code that’s sent to your phone after inputting your login information.
- Be cautious of links or attachments from unreliable sources: Malware often lurks in email attachments or links. Before clicking on a link or opening an attachment, verify that you know the sender and check for signs of phishing. Never open an attachment from someone you don’t know.
- Scan attachments, even from encrypted email: Use antivirus software or an online service to scan your email attachments and look for malware before you open them.
- Keep software updated: Regularly updating your operating system, web browser and other software patches security vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit. Updates often include important security fixes.
- Use a VPN: A virtual private network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic and masks your IP address, adding an extra layer of privacy and security, especially when using public Wi-Fi. A VPN can help protect your data from being intercepted during transit.
- Be mindful of social media settings: Limit the personal information you share on social media. Hackers can use this information to guess passwords or launch social engineering attacks. Be aware of what you’re sharing publicly.
- Avoid checking emails on public Wi-Fi: Cybercriminals can monitor your online activities and steal your personal information on public Wi-Fi, so avoid logging into accounts like email or your bank accounts if possible.
Communicate Confidently With Panda Security
With everything accessible online, protecting your sensitive information is essential. By taking proactive steps to encrypt your emails, you’re not only safeguarding your personal information but also contributing to a more secure online environment.
However, strong email security is just one piece of the puzzle. Comprehensive protection requires a multi-layered approach, and Panda Dome Complete antivirus provides that extra shield with features like real-time threat detection, a powerful firewall and even safe browsing for phishing protection. Don’t leave your digital life vulnerable — get protected with Panda Dome today.
FAQ
Have more questions about email encryption and security? Here are answers to some frequently asked questions to help you understand how you can protect your emails and ensure your sensitive information stays secure.
Can I Encrypt Individual Emails or Do I Need To Encrypt All Messages by Default?
You can encrypt individual emails, you don’t have to encrypt all messages by default. Here’s how to send secure messages on various platforms:
- Gmail: You can choose to turn on Confidential Mode for individual emails. If you’re using third-party encryption like FlowCrypt, you can encrypt just the emails you want.
- Outlook: You can turn encryption on per email from the “Options” tab. No need to encrypt every message unless you set it up that way in admin settings (e.g. via Microsoft 365 compliance policies).
- Yahoo: Yahoo Mail doesn’t offer built-in end-to-end encryption. To send an encrypted email, you’ll need a third-party tool like Mailvelope (PGP-based), ProtonMail Bridge, or another encryption plugin. Once set up, you can encrypt individual messages before sending.
How Can You Password-Protect an Email?
To password-protect an email, use a third-party encryption tool or an email service with built-in password-protection features. For example, services like Proton Mail allow you to set a password for the recipient to decrypt and view the message. You can also create a password-protected PDF or document to attach to your email as an alternative.
Is Email Encryption Foolproof?
Email encryption is a powerful tool, but it’s not 100% foolproof. While it makes your emails much harder to read if intercepted, it doesn’t guarantee security. Think of it as a strong lock on your door — it deters most intruders, but a determined thief might still find a way in.
To really boost your email security, combine encryption with other best practices. Use strong, unique passwords, enable two-factor authentication, be wary of suspicious links and attachments, keep your software updated and consider using a VPN, especially on public Wi-Fi. A layered approach like this will give you much better protection than encryption alone.
What Does Encrypting an Email Do?
Encrypting an email transforms its content into unreadable code, ensuring only the intended recipient can decipher it using a private key. This prevents unauthorized access, even if the message is intercepted during transit.
Does Both the Sender and Recipient Need to Use the Same Encryption Method?
Both the sender and recipient need to use compatible encryption methods for encrypted email to work. The sender uses the recipient’s public key (part of their digital certificate) to encrypt the message, and the recipient uses their corresponding private key to decrypt it. If the sender and recipient use different, incompatible methods, they won’t be able to communicate securely.
What Is the Difference Between Encryption and Digital Signatures?
Encryption scrambles the content of a message to keep it secret, while a digital signature provides authentication and ensures the message hasn’t been tampered with. Essentially, encryption protects the content, while digital signatures protect the integrity and origin of the message.






