Worms and viruses are both types of malware. Worms are more self-sufficient and spread independently through networks, while viruses need human help and a host file or program to spread.
Worms, viruses, bots, oh my! Such names sound less like monikers for malicious software than characters in a sci-fi novel. Despite their fictional-sounding names, the monetary damage these types of malware can cause to computers and data is very real. Studies put the global cost of data breaches for 2024 at $4.88 million.
Worms and viruses are malware designed to harm computers or networks. Worms spread automatically across networks, while viruses need a host file or program to latch onto. If your computer isn’t protected, both can cause damage — whether by stealing data, disrupting operations, or making your device unusable.
Learn the differences between them and how they work to limit the damage of a malware attack and avoid infection altogether.
Malware vs. Virus vs. Worm
Malware comes in many forms, but two of the most common types are viruses and worms. These threats can infect your computer, steal data and disrupt operations. Let’s take a look at the main differences between malware, computer worms and viruses.
Malware
Think of malware as a sneaky intruder trying to break into your home. Some use different methods, but the goal is always the same: to cause damage or steal something valuable. Malware encompasses all harmful software — whether it sneaks in through a suspicious link, an infected file or a network vulnerability. Its purpose can range from stealing your data to locking you out of your system for ransom.
Virus
A virus is a type of malware, acting like a thief hiding inside a harmless-looking package. You have to open the package (or file) for it to do damage. Once activated, the virus can spread to other files and even devices, corrupting data and causing chaos — remember Friday the 13th? A virus is like a booby-trapped gift that looks innocent but can release a harmful surprise when opened.
Worm
A worm is like an intruder who doesn’t need to be invited in. It slips in through unlocked windows and doors (network vulnerabilities) and spreads itself across the house (network) without any help from you. Computer worms can quickly multiply, infecting many devices at once, causing widespread damage, making worm malware a particularly dangerous threat.

Which Is More Dangerous: Malware, Viruses or Worms?
When it comes to threats, both viruses and worms can cause serious damage, but worms often present a bigger risk due to their ability to spread independently. A virus requires human action — such as opening an infected file — to activate and spread. While still harmful, virus spread is more controlled and can sometimes be easier to contain.
Worms, on the other hand, don’t need any help. They can quickly move through networks, replicating themselves and infecting multiple devices in a short amount of time. This makes worm malware particularly dangerous, especially for businesses with interconnected systems.
Without antivirus protection, the risk of a malware attack skyrockets. Antivirus software acts as a defense, detecting and blocking these threats before they can enter your system. Without it, your devices are left vulnerable to attacks — whether it’s from a virus you accidentally trigger or a worm that slips into your network unnoticed. Install an antivirus to reduce the likelihood of an attack.
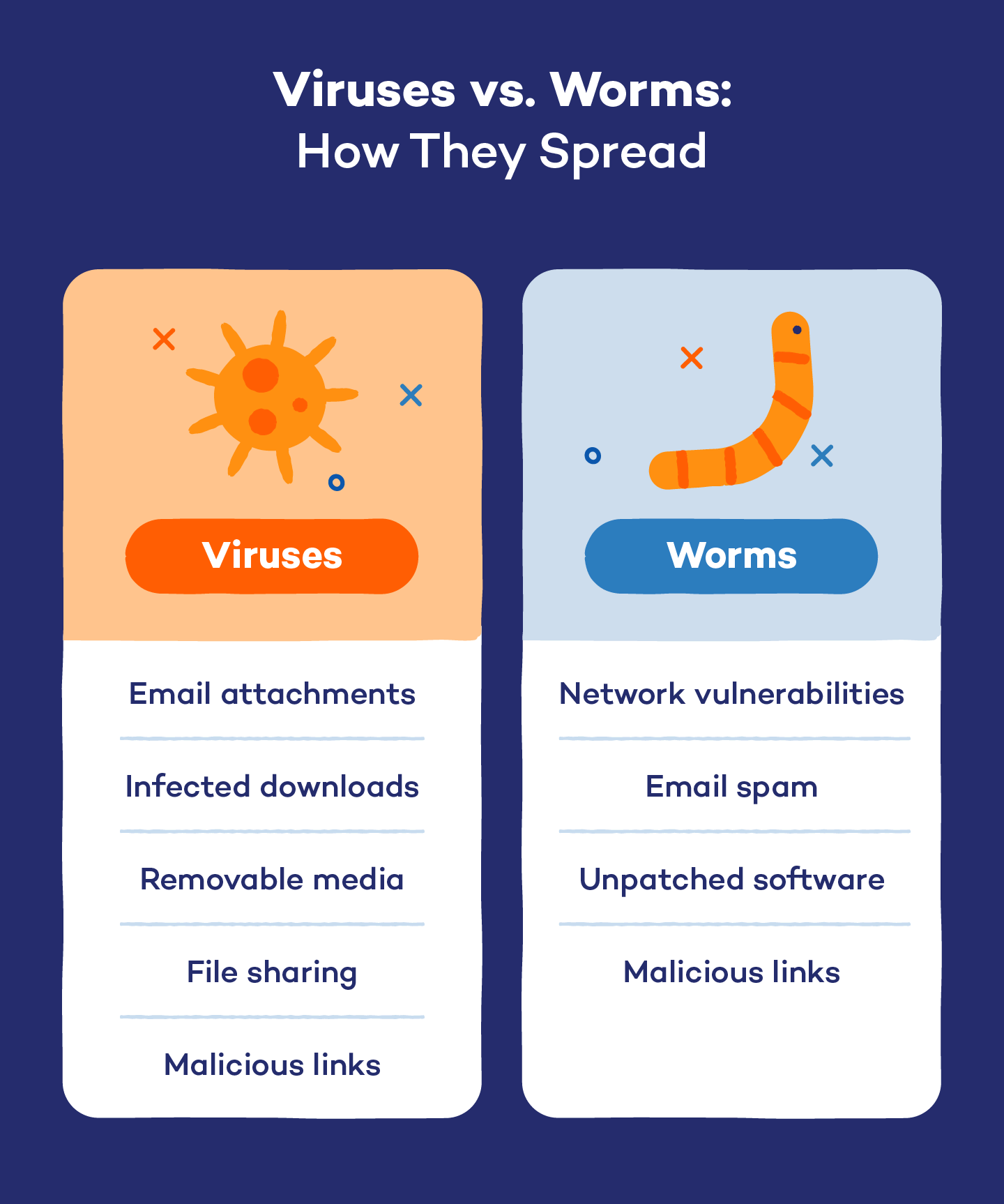
How Viruses and Worms Spread
It takes human action to replicate a virus. Even iPhones can get infected, which revolve around security and data privacy. Here are the main ways viruses can infiltrate your system:
- Email attachments: Many viruses are sent as infected attachments. Opening these files can activate the virus.
- Infected downloads: Downloading software or files from untrustworthy sources can introduce viruses that hide within seemingly legitimate downloads.
- Removable media: USB drives and external hard drives can carry viruses. Plugging in an infected device can transfer the virus to your computer.
- File sharing: Sharing files over peer-to-peer networks can lead to virus infections, especially if the files come from unverified sources.
- Malicious links: Clicking on links in emails or on websites can lead to virus downloads or redirection to malicious sites that install malware.
Just like viruses, clicking on malicious links can lead to worm infections, especially if they exploit network flaws. Here are some other ways worms can spread:
- Network vulnerabilities: Worms exploit security gaps in networks. Once a worm enters, it replicates and spreads to other connected devices without user interaction.
- Email spam: Some worms can spread through spam emails, using infected attachments or links to replicate themselves when opened.
- Unpatched software: Worms often target unpatched software vulnerabilities. Keeping software updated is essential to prevent this type of spread.
How Social Engineering Spreads Malware
Social engineering is a way of tricking people into spreading malware to others, and both viruses and worms often rely on tricking users into taking action, such as opening a file or clicking a link. Hackers use your own assumptions and confirmation bias to fool you.
For example, when you visit your bank’s website, you usually first look for the most recognizable features: company name, logo and the familiar layout of the page. All of these features tip you off that you’re in the right place. Instead of applying a more critical eye, you quickly compare what you see to what you expect. When those basic expectations are confirmed, you click ahead.
Every day, hackers create malicious copies of legitimate websites and emails to steal our private credentials. These digital fakes don’t need to be perfect copies either, just close enough to match our expectations. That’s why it’s best to avoid clicking email links to common websites and instead use a browser bookmark so you always know you’re in the right place.
Worms Spread Differently From Other Viruses
Worms are passed through files like attachments or website links, but have the ability to self-replicate. They can clone and transmit themselves to thousands of other computers without any help from humans. Consequently, worms tend to spread exponentially faster than viruses.
Worms have this viral superpower in part because they don’t rely on a host file like a virus. While viruses use these files and programs to run, worms only need them as disguises to sneakily wiggle into your computer. After that, the worm runs the show. No more host files or social engineering required.
How to Protect Yourself From Worms and Viruses
Even though worms and viruses are different, you take similar precautions to avoid them, such as avoiding unfamiliar attachments, keeping your OS updated and protecting your devices with antivirus or anti-malware.

Avoid Opening Unfamiliar Messages and Attachments
Like we said earlier, social engineering preys on our assumptions and familiarity, but you can fight it by paying more attention to your online interactions. Inspect emails closely. Phishing emails usually have telltale signs they’re scams. Most importantly, never open an email attachment from an unknown source. If you can’t confirm the source, delete the attachment. One moment of satisfying your curiosity isn’t worth the risk.
Avoid Nonsecure Webpages
Nonsecure websites don’t encrypt how they talk to your browser like secure ones do. It’s easy to identify websites that are nonsecure. They start with HTTP in their URL address. Try to visit only secure sites that start with HTTPS. The “s” stands for “secure.” Browser plugins like HTTPS Everywhere can make searching only HTTPS sites easier.
Update Your Operating Systems
Hackers love to find security holes in operating systems like Windows. It’s a game of cat and mouse played with software engineers who constantly test, identify and patch ways of infiltrating their own software. The result of their efforts is the security update. Updating your OS applies those patches as soon as they’re released, increasing your protection level. Setting your system to auto-update is also a smart way to avoid viruses.
Be Picky About Your Programs
Like operating systems, individual apps on your devices also need updating — and for the same reason. Aside from updating them, you should also decide whether you even need them at all. Remember, viruses need host files and programs for execution and disguise. Decide whether you actually need the app, or if you already have it, how often you use it. The more apps you have, the more updates you’ll need to do. The more updates, the more opportunities for a security breach or infection.
A couple of programs you will want to give special attention to are Adobe Flash and Acrobat Reader. Both are popular targets for cybercriminals. If you don’t use them, uninstall them.
Get Antivirus Protection
The easiest and most effective action you can take to protect yourself from worms and viruses is to get a total antivirus protection plan. Antivirus software can’t be manipulated by social engineering tricks. It never assumes anything. It scans every file you open and every program you run for viruses and worms. Good ones do this in real time.
Every worm and virus discovered gets assigned a “signature,” a unique indicator that says “This is a virus!” Antivirus software keeps a list of those signatures and compares them to all of the data coming through your system.
You now understand the differences between worms and viruses, how they spread and where they hide. Be more critical the next time you open an unfamiliar email or visit a familiar website. Following these tips and getting antivirus, including for MacBook, is the best way to avoid malware.
Worm vs. Virus FAQ
Let’s dive into some common questions about worms and viruses to clear up any confusion. Understanding these threats is super important for keeping your digital life secure.
What Is the Difference Between Worms and Viruses?
Worms and viruses are both types of malware, but they differ in how they spread. A virus attaches itself to a host file and requires user action to activate, while a worm can replicate and spread independently across networks without any human intervention. This makes worms generally more aggressive in their ability to infect multiple devices quickly.
How Do You Know if You Have a Worm Virus?
The term “worm virus” is often mistakenly used, but technically, it’s a misnomer. Worms and viruses are distinct types of malware, and there’s no specific malware called a worm virus. Identifying both can be tricky, but common signs include sluggish system performance, unexpected crashes and unusual network activity.
What Are 5 Examples of Worms?
Notable computer worms include ILOVEYOU, Conficker, Sasser, Mydoom and Nimda, each causing significant damage through methods like email attachments and exploiting system vulnerabilities.
How Is a Worm Different From a Trojan?
A worm is a type of malware that can replicate and spread independently across networks without any user action, while a Trojan disguises itself as legitimate software to trick users into downloading it. Unlike worms, Trojans do not self-replicate; instead, they rely on users to execute the harmful program, which can lead to data theft or system compromise.








