Ransomware is a type of malware that threatens to destroy or withhold a victim’s critical data unless a ransom is paid to the attacker. Unfortunately, cyberattacks are on the rise as we see 71% year-over-year increase in cyberattacks.
Ransomware attacks are more prevalent than ever, and they’re wreaking havoc across a range of industries, including construction, health care, finance, and more. There were 4,611 cases reported in 2023 — a nearly 73% jump from the 2,662 cases in 2022.
Read on to learn about the most important ransomware statistics that will be vital for security in 2024 and beyond, along with prevention tips and how to ensure your organization is prepared for an attack.
Key Ransomware Attack Trends
As the cyber threat landscape continues to evolve, a few key trends can be seen in the ongoing rise of ransomware attacks.
The Rise of Double Extortion: Attack Methods Are Evolving
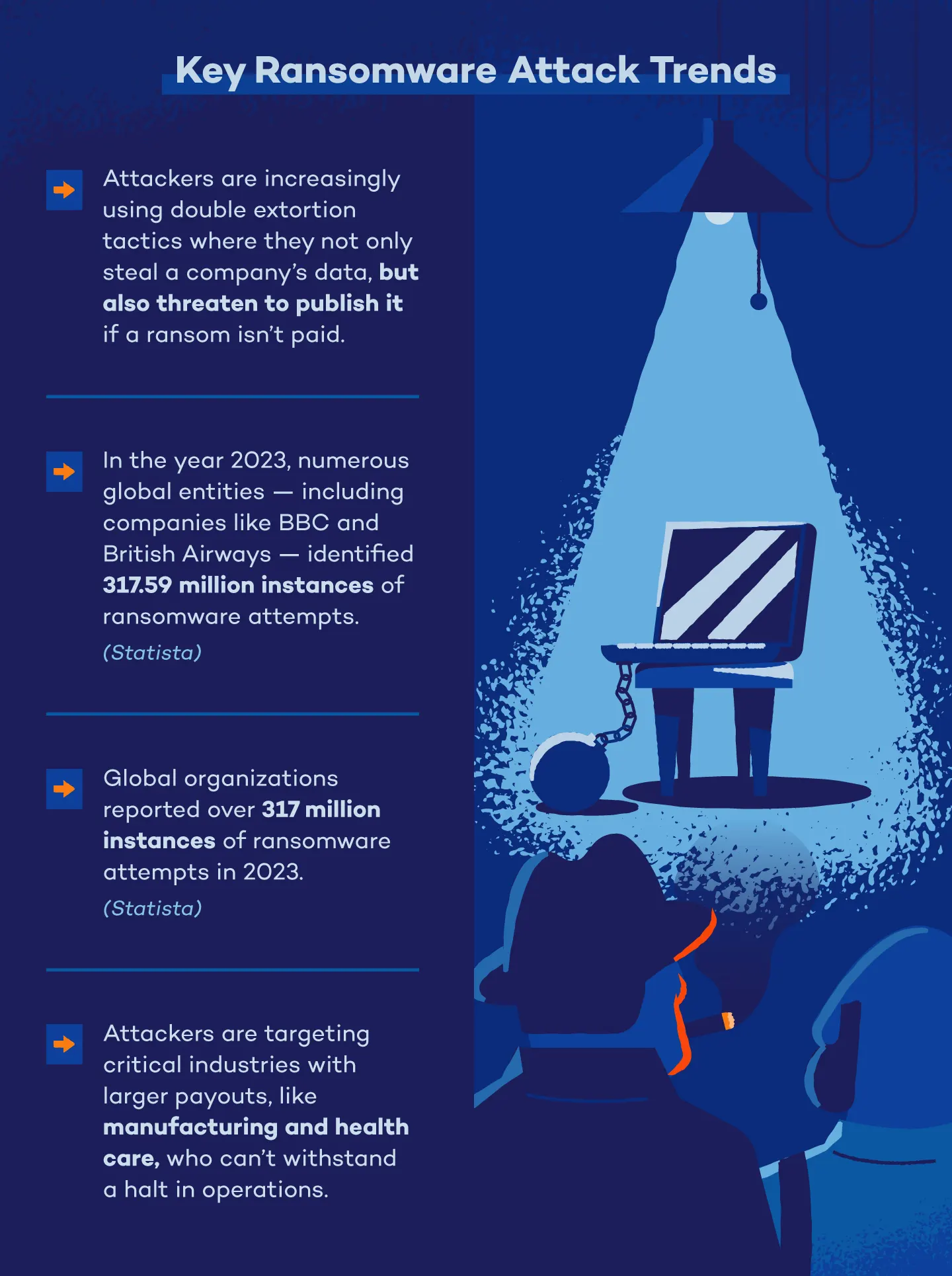
In years past, ransomware was mainly accomplished by single extortion, where attackers encrypt an organization’s data and demand a ransom in exchange for a decryption key. Now, ransomware groups are exfiltrating victims’ data to an offsite location before encryption, then threatening to leak or publish the data if a ransom isn’t received. The combined threat of encryption and data exfiltration is a form of double extortion, and threat actors are increasingly leveraging this attack method as it proves to be more profitable.
Ransom Demands Are Increasing
As new approaches to ransomware like double extortion continue to pay off, attackers are demanding higher ransom payouts than ever before.
In 2023 alone, numerous global entities — including victims like BBC and British Airways — reported over 317 million instances of ransomware attempts.
Increase in Ransomware-as-a-Service
While home users were once the main target for ransomware attacks, threat actors today are targeting large enterprise networks with more frequency. As a result, the evolution of ransomware-as-a-service, or RaaS, has gained increasing traction.
RaaS is a type of pay-for-use malware that allows cybercriminals to purchase ransomware tools that have already been developed in order to carry out large-scale ransomware attacks. RaaS is an affiliate program in nature — for every successful ransom payment made, the creators of the tools receive a percentage.
Since RaaS allows cybercriminals with even elementary technical skills to deploy a ransomware attack, the RaaS business model will continue to fuel the threat landscape in 2023.
The Industrial Goods and Services Sector Is the Largest Target
In January 2023, Royal Mail — a British postal and courier company — faced a ransomware attack orchestrated by the LockBit group. The attackers listed the company on their extortion site and set a deadline for payment. The attack, which halted international parcel deliveries, threatened to publish unspecified data if demands were not met.
Despite assurances from Royal Mail that no sensitive customer information has been compromised, the incident has impacted the company’s share value and operations. While Royal Mail works to restore services, British cyber authorities emphasize the importance of resilience and recovery in combating the increasing threat of ransomware attacks across the U.K.
How Common Were Ransomware Attacks in 2022-2023?
In 2024, 59% of organizations experienced ransomware attacks, showing a slight decline from the 66% reported in each of the preceding two years.
1. In 2023, researchers at SonicWall Capture Labs documented a total of 6.06 billion malware incidents, marking an 11% rise from the previous year. (SonicWall)
2. In 2022, roughly 68% of the worldwide reported cyberattacks were ransomware. (Statista)
3. The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) recently disclosed a new high of 880,418 internet crime complaints in 2023. Among these, ransomware complaints surged by 18% to reach 2,825 cases. (IC3)
4. There was 27% more ransomware in the second half of 2023 than the first half. (SonicWall)
5. Ransomware attacks in Asia reached an all-time high in 2023, soaring to 17.5 million — a staggering 1,627% jump from 2019. (SonicWall)
6. In 2023, the number of ransomware attempts kept rising, reaching 7.6 trillion, marking a 20% increase compared to the total in 2022. (SonicWall)
7. During the second quarter of 2023, ransomware attacks in global organizations saw 34% of cases leading to a ransom payment, a decrease from 45% in the preceding quarter. (Statista)
8. In 2022, Stop/Djvu ranked as the most frequently encountered ransomware Trojan, representing over 16% of all encounters. (Statista)
9. Twenty-six new ransomware families were discovered in 2022, representing a 66% YoY decrease. (Statista)
10. There were 317.59 million ransomware attacks globally in 2023. (Statista)
11. Between the last two quarters of 2022, there was a surge of over 50% in global ransomware attacks, rising from over 102 million to nearly 155 million cases. (Statista)
12. In 2023, the highest number of attacks occurred in November, totaling 89 incidents, trailed by December and September, each with 70 attacks. (Blackfog)
13. In 2022, businesses employing 100 or more workers faced ransomware attacks at a rate of 56%, down from 70% in the previous year. (Delinea)
Ransomware Cost and Payment Statistics
When it comes to the cost of ransomware, cybercriminals are making and demanding more money than ever before. Take a look at cost and payment trends for ransomware below:
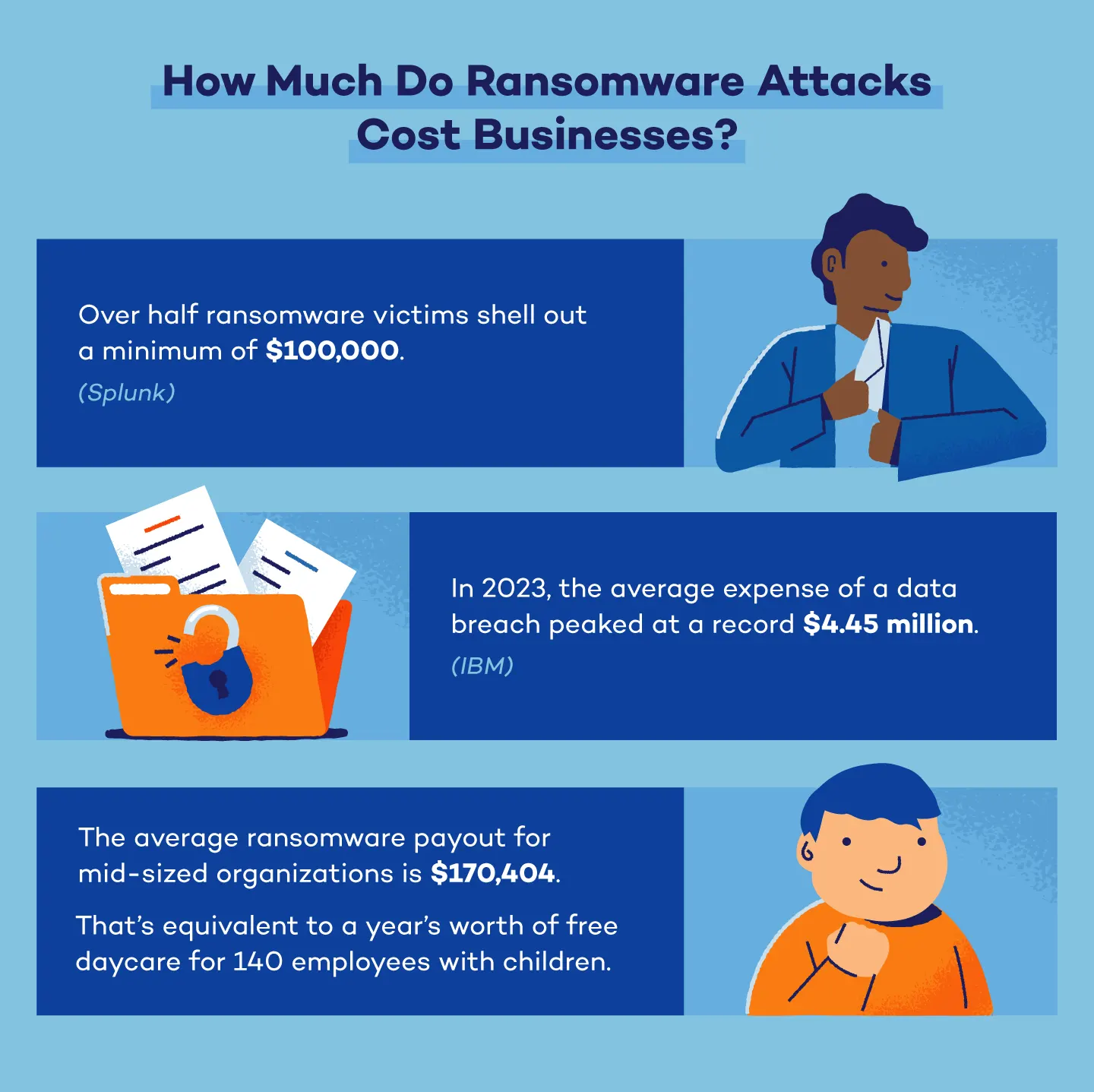
14. A total of 83% of victims responded to ransomware attacks by paying the attackers, either directly, through cyber insurance, or via a negotiator. Among them, over half shelled out a minimum of $100,000. (Splunk)
15. The largest sum paid fell within the range of $25,000 to $99,999, accounting for 44% of payments. (Splunk)
16. In 2023, the average expense of a data breach peaked at a record $4.45 million. (IBM)
17. Half of organizations intend to boost security spending following a breach. (IBM)
18. In 2023, smaller organizations with fewer than 500 employees observed a rise in the average impact of a data breach from $2.92 million to $3.31 million, marking an increase of 13.4%. (IBM)
19. In 2022, there was an 11.22% increase quarter over quarter in the third quarter for ransomware incidents, alongside a significant 95.41% YoY rise in activity on leak sites. (Corvus)
20. In 2023, total ransomware payments exceeded $1 billion. (Ransomware)
21. In the fourth quarter of 2023, the percentage of ransomware victims who paid ransom demands hit an all-time low of 29%. (Ransomware)
22. Thirty-three percent of organizations indicated they would consider paying ransom on a case-by-case basis. (Ransomware)
23. In 2023, only 7% of organizations intended to notably boost their investment in technologies to defend ransomware for the upcoming year. (Ransomware)
24. Thirty-eight percent of organizations plan to maintain their current investment levels for ransomware defense. (Ransomware)
25. In the second quarter of 2023, there was a more than twofold increase in the average ransom paid, rising from around $328,000 in the first quarter of 2023 to over $740,000 in the second quarter of 2023. (Statista)
Attacks by Ransomware Group
Both old and new ransomware groups are wreaking havoc on industries across the globe, but a few stood out from the rest:
26. LockBit emerged as the most prevalent ransomware group in 2023, dominating the landscape with 19.2% of reported attacks. (Blackfog)
27. Following closely behind, BlackCat was responsible for 18.4% of ransomware incidents. (Blackfog)
28. Medusa posed a notable threat, accounting for 5.5% of ransomware attacks in 2023. (Blackfog)
29. Play was responsible for 4.6% of reported ransomware occurrences in 2023. (Blackfog)
30. LockBit and BlackCat together represented a significant portion, amounting to 38% of all reported ransomware attack variants in 2023. (Blackfog)
31. LockBit witnessed a notable increase of 3.5%, while BlackCat experienced a substantial surge of 5.4% in reported attack occurrences. (Blackfog)
Attacks by Industry
No industry is safe from ransomware attacks. Let’s look at how different industries have been impacted between 2022 and 2024.
Health care
32. In 2024, the health care sector saw a 7% rise in the attack rate over the past year. (Sophos)
33. In 2024, malware targeting health care spiked by 20%. (SonicWall)
34. The health care sector was among five industries showing a rise in attack frequency from 2023 to 2024, climbing from 60% to 67%. (Sophos)
35. In 2023, 39% of health care organizations ended up paying more ransom than what was initially demanded. (Sophos)
36. In 2023, health care was one of the top infrastructure sectors affected by ransomware. (IC3)
Education
37. Education, which encountered the highest amount of malware in 2022, witnessed a 3% decrease in 2023. (SonicWall)
38. Moderate and high-severity ransomware incidents surged by 19% in 2023. (SonicWall)
39. Between 2022 and 2024, the education industry paid a median ransom of $6.6 million. (Sophos)
40. Sixty-seven percent of higher education organizations end up paying more ransom than what was initially demanded in 2023. (Sophos)
Government
41. Thirty-four percent of government organizations reported being hit by a ransomware attack in 2023. (Sophos)
42. In 2023, malware targeting government organizations spiked 38% since 2019. (SonicWall)
43. Moderate and high-severity ransomware incidents surged by 46% in 2023. (SonicWall)
44. In 2024, the central/federal government sector reported a 68% attack rate among all industries. (Sophos)
Other Industries
45. Out of 1,829 cyber incidents reported by financial institutions globally in 2022, 477 resulted in the exposure of sensitive data. (Statista)
46. In 2023, 55% of IT organizations were hit with a ransomware attack. (Sophos)
47. Malware attacks on the finance sector doubled in 2023 compared to the previous year. (SonicWall)
Global Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks spiked across the globe. Let’s have a look at some worldwide statistics:
48. France reported the highest rate of ransomware attacks in 2024 at 74%. (Sophos)
49. South Africa followed closely behind with 69%, while Italy reported 68%. (Sophos)
50. Conversely, the lowest attack rates were reported in Brazil (44%), Japan (51%), and Australia (54%). (Sophos)
51. Overall, nine countries saw a decrease in attack rates compared to 2023. (Sophos)
52. Five European countries, including Austria, France, Germany, Italy, and the U.K. (with Germany’s increase being less than 1%), reported higher attack rates. (Sophos)
Ransomware Predictions and Future Trends
Ransomware is evolving at a rapid pace and will continue to impact all industries in 2024 and beyond. Looking ahead, these statistics shed light on the projections and future trends for ransomware.
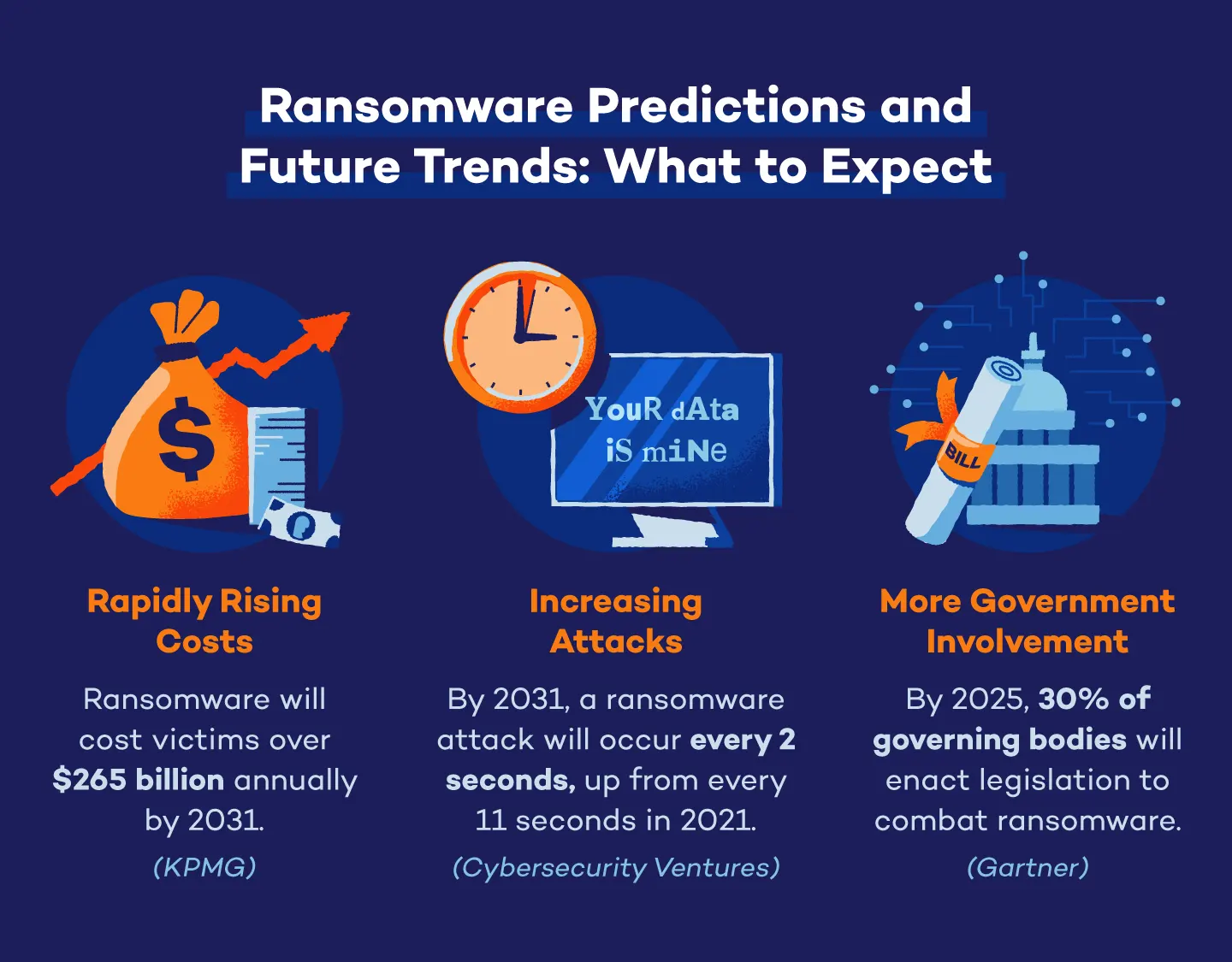
53. Sixty percent of organizations, along with investors and venture capitalists, will use cybersecurity risk as a key factor in assessing new business opportunities by 2025. (Gartner)
54. By 2025, 30% of nation states will enact legislation to regulate ransomware payments and negotiations. (Gartner)
55. Forty percent of boards of directors will have a cybersecurity committee by 2025 as stricter cybersecurity measures become a top priority. (Gartner)
56. Seventy percent of CEOs will invest in an organizational culture of cyber resilience by 2025. (Gartner)
57. IoT devices are predicted to be increasingly used by attackers to carry out ransomware attacks in 2023 and beyond. (RSA Security via Security Boulevard)
58. Yearly revenue for the corporate web security industry has increased annually since 2016 and is expected to reach nearly $8 billion by 2025. (Statista)
How to Prevent a Ransomware Attack
Defending against ransomware attacks is similar to protecting against other types of cyberattacks. The main difference is that ransomware represents a far higher risk to organizations, so taking the proper precautions should be front of mind in securing your organization’s data and assets.
Invest in Employee Education
Cybersecurity is ultimately a human problem, and fostering internal awareness of how to identify a potential ransomware attack is a critical first line of defense for organizations. A threat can’t be avoided if it can’t be recognized, and educating your teams on how to identify potential cyber threats can significantly reduce the chances of an attack. Investing in ongoing cybersecurity training should be a priority for organizations that want to become more cyber resilient.
Implement Endpoint Protections
One of the most effective protections against ransomware and other types of malware is endpoint security, which involves securing endpoints and entry points for all enterprise devices within your organization. Protections like URL filtering and anti-phishing solutions can drastically reduce the chances of infection from common ransomware variants, and they should be deployed on all devices for all users within the organization.
Use a Strong Password Manager
Password security is essential to protecting your organization’s data, but many companies fail to implement proper password use and management across their teams. This simple line of defense can drastically reduce the chances of a ransomware attack or any other cyberattack, and organizations that prioritize a strong password management system will be more successful in preventing an attack.
Keep Reliable Offsite Backups
Organizations should ensure they regularly back up their data and that they have a recovery process in place. Since ransomware attackers often target on-site backups for encryption, ensuring all backups are maintained in a secure offline location is crucial.
Ransomware isn’t anything new, but the last year has revealed its establishment as a highly effective and lucrative attack method for criminals to exploit. Hopefully, the explosive increase and evolution of ransomware in recent years will serve to disrupt the widespread indifference to security issues historically seen across organizations of all industries.
Organizations who prioritize properly securing their data will be more successful in defending against an attack in 2023 and beyond. Something as simple as implementing an endpoint security solution across all enterprise devices will equip you to protect, detect and respond to cyberattacks as the threat landscape continues to evolve.

The global landscape of ransomware attacks continues to evolve, with certain regions experiencing heightened vulnerabilities and others demonstrating resilience. It’s imperative for organizations to stay vigilant and prioritize robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against these threats.
To ensure comprehensive protection for your devices, explore Panda Dome antivirus plans designed to provide peace of mind in an increasingly digital world.




